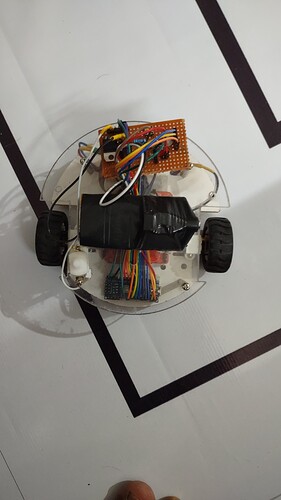
Hello, I have made line following bot successfully and now I am trying to make maze solving part. I had gone through the 3pi maze solving code and implemented it, it follows the path successfully but it is taking problems while at the dead end.
It does turn around at the dead but sensor don’t come on the line once turn around. I have increased the delay but also it causing problems.
At some intersections only left/right intersections it move forward a little bit Frome the line it tries to turn left or right but don’t able to take it meanwhile it runs the turn around module.
@Ben @BrandonM Please guide me what should I do to move accurately.
Hello.
That looks great! Thank you for sharing.
It sounds like your robot is mis-identifying intersections. In the original 3pi maze solving code, once an intersection has been detected, the robot drives forward for a small amount of time, checks the left- and right-most sensors (for turns), then drives forward for a small amount of time again and checks the center sensors (for a straight path or finish). I suspect that you need to tune the timing of the two “drive forward” steps, since your robot and the 3pi are probably not similar enough for it to work with the same values.
For example, if it reaches a left or right turn and turns around instead, it might be going too far forward before taking the reading, so you could try reducing the delay and/or speed of the movement before reading the line sensors.
Brandon
@BrandonM I have adjusted delays but also it creating problems while turning. I have attached the video and the code.
#include <QTRSensors.h>
#define PWM1 5 //LEFT MOTOR
#define AIN1 7
#define AIN2 8
#define PWM2 6 //RIGHT MOTOR
#define BIN1 4
#define BIN2 9
#define pushButton 2
QTRSensors qtr;
const uint8_t SensorCount = 8;
uint16_t sensorValues[SensorCount];
int dir_motor = 1;
int turnSpeed = 105; //110
char path[100] = "";
unsigned char path_length = 0; // the length of the path
int range = 150;
void setup(){
// configure the sensorValues
qtr.setTypeAnalog();
qtr.setSensorPins((const uint8_t[]){A7, A6, A5, A4, A3, A2, A1, A0}, SensorCount);
delay(500);
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BIN1,OUTPUT);
pinMode(AIN1,OUTPUT);
pinMode(AIN2,OUTPUT);
pinMode(BIN2,OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWM1,OUTPUT);
pinMode(PWM2,OUTPUT);
pinMode(pushButton, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(12,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(12, HIGH);
pinMode(3,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(3, HIGH);
delay(3000);
calibrationMode();
delay(2000);
/*int buttonState = digitalRead(pushButton);
//Serial.println(buttonState);
if (buttonState == 1) {
delay(2000);
calibrationMode(); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
}*/
}
void loop(){
maze_solve();
//follow_segment();
}
void set_Motors( int x, int y){
if(x>=0){
//FORWARD//LEFT MOTOR
digitalWrite(AIN1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(AIN2,LOW);
//Speed control of Motor LEFT
analogWrite(PWM1,x);
}
else if(x<0){
//FORWARD//LEFT MOTOR
digitalWrite(AIN1,LOW);
digitalWrite(AIN2,HIGH);
//Speed control of Motor LEFT
analogWrite(PWM1,-x);
}
if(y>=0){
//FORWARD//RIGHT MOTOR
digitalWrite(BIN1,HIGH);
digitalWrite(BIN2,LOW);
//Speed control of Motor LEFT
analogWrite(PWM2,y);
}
else if(y<0){
//FORWARD//LEFT MOTOR
digitalWrite(BIN1,LOW);
digitalWrite(BIN2,HIGH);
//Speed control of Motor LEFT
analogWrite(PWM2,-y);
}
}
void follow_segment()
{
int last_proportional = 0;
long integral=0;
float Kp = 0.30; //0.1 // for maxspeed= 180, Kp=0.40, Ki=0.00001, Kd = 8.55
float Ki = 0.000001;
float Kd = 1.4; //1.2//20 //for max speed =140, kp = 0.40, kd= 6//1.4
while(1)
{
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < SensorCount; i++){
}
// Get the position of the line.
unsigned int position = qtr.readLineBlack(sensorValues);
//Serial.println(position);
// The "proportional" term should be 0 when we are on the line.
int proportional = ((int)position) - 3500;
//Serial.println(proportional);
// Compute the derivative (change) and integral (sum) of the
// position.
int derivative = proportional - last_proportional;
integral += proportional;
// Remember the last position.
last_proportional = proportional;
// Compute the difference between the two motor power settings,
// m1 - m2. If this is a positive number the robot will turn
// to the left. If it is a negative number, the robot will
// turn to the right, and the magnitude of the number determines
// the sharpness of the turn.
int power_difference = proportional*Kp + integral*Ki + derivative*Kd;
// Compute the actual motor settings. We never set either motor
// to a negative value.
const int max = 120; // the maximum speed//150
if(power_difference > max)
power_difference = max;
if(power_difference < -max)
power_difference = -max;
//Serial.println(power_difference);
if(power_difference < 0)
set_Motors(max+power_difference,max);
else
set_Motors(max,max-power_difference);
// We use the inner three sensorValues (1, 2, and 3) for
// determining whether there is a line straight ahead, and the
// sensorValues 0 and 4 for detecting lines going to the left and
// right.
qtr.read(sensorValues);
if(sensorValues[2] < 100 && sensorValues[3] < 100 && sensorValues[4] < 100 && sensorValues[5]<100 && sensorValues[6] < 100 && sensorValues[7] < 100 && sensorValues[0] < 100 && sensorValues[1]<100)
{
// There is no line visible ahead, and we didn't see any
// intersection. Must be a dead end.
//Serial.println("DEAD END");
return;
}
/*if((sensorValues[0] > 200 && sensorValues[7] > 200) || (sensorValues[1] > 200 && sensorValues[6] > 200) || (sensorValues[1] > 200 && sensorValues[2] > 200 &&
sensorValues[3] > 200) || (sensorValues[6] > 200 && sensorValues[5] > 200 && sensorValues[4] > 200))
{ // Found an intersection.
//Serial.println("INTERSECTION");
return;
}*/
if((sensorValues[5] > 200 && sensorValues[6] > 200) || (sensorValues[1] > 200 && sensorValues[2] > 200))
{ // Found an intersection.
//Serial.println("INTERSECTION");
return;
}
}
}
void calibrationMode(){
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // turn on Arduino's LED to indicate we are in calibration mode
analogWrite (PWM1, 150);
analogWrite (PWM2, 150);
// analogRead() takes about 0.1 ms on an AVR.
// 0.1 ms per sensor * 4 samples per sensor read (default) * 8 sensorValues
// * 10 reads per calibrate() call = ~32 ms per calibrate() call.
// Call calibrate() 100 times to make calibration take about 3.2 seconds.
for (uint16_t i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
qtr.calibrate();
if (i % 20 == 0){
//dir_motor = -dir_motor;
//change_direction(dir_motor);
}
}
analogWrite (PWM1, 0);
analogWrite (PWM2, 0);
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); // turn off Arduino's LED to indicate we are through with calibration
}
void change_direction(int dir){
if (dir == 1) {
digitalWrite (AIN1, HIGH);
digitalWrite (AIN2, LOW);
analogWrite (PWM1, 100);
digitalWrite (BIN1, LOW);
digitalWrite (BIN2, HIGH);
analogWrite (PWM2, 100);
}
else {
digitalWrite (AIN1, LOW);
digitalWrite (AIN2, HIGH);
analogWrite (PWM1, 100);
digitalWrite (BIN1, HIGH);
digitalWrite (BIN2, LOW);
analogWrite (PWM2, 100);
}
}
// Turns according to the parameter dir, which should be 'L', 'R', 'S'
// (straight), or 'B' (back).
void Turn(char dir)
{
switch(dir)
{
case 'L':
// Turn left.
set_Motors(-turnSpeed,turnSpeed);
delay(265);
break;
case 'R':
// Turn right.
set_Motors(turnSpeed,-turnSpeed);
delay(255); //255//260
break;
case 'B':
// Turn around.
set_Motors(70,-70); //80
delay(860); //810//850//870
break;
case 'S':
// Don't do anything!
break;
}
}
char select_turn(unsigned char found_right, unsigned char found_straight,unsigned char found_left)
{
// Make a decision about how to turn. The following code
// implements a left-hand-on-the-wall strategy, where we always
// turn as far to the left as possible.
if(found_right)
return 'R';
else if(found_straight)
return 'S';
//else if(found_back)
//return 'B';
else if(found_left)
return 'L';
else
return 'B';
}
void simplify_path()
{
// only simplify the path if the second-to-last turn was a 'B'
if(path_length < 3 || path[path_length-2] != 'B')
return;
int total_angle = 0;
int i;
for(i=1;i<=3;i++)
{
switch(path[path_length-i])
{
case 'R':
total_angle += 90;
break;
case 'L':
total_angle += 270;
break;
case 'B':
total_angle += 180;
break;
}
}
// Get the angle as a number between 0 and 360 degrees.
total_angle = total_angle % 360;
// Replace all of those turns with a single one.
switch(total_angle)
{
case 0:
path[path_length - 3] = 'S';
break;
case 90:
path[path_length - 3] = 'R';
break;
case 180:
path[path_length - 3] = 'B';
break;
case 270:
path[path_length - 3] = 'L';
break;
}
// The path is now two steps shorter.
path_length -= 2;
}
// This function is called once, from main.c.
void maze_solve()
{
// Loop until we have solved the maze.
while(1)
{
// FIRST MAIN LOOP BODY
follow_segment();
// Drive straight a bit. This helps us in case we entered the
// intersection at an angle.
// Note that we are slowing down - this prevents the robot
// from tipping forward too much.
set_Motors(30,30);
delay(8); //40//20
// These variables record whether the robot has seen a line to the
// left, straight ahead, and right, whil examining the current
// intersection.
unsigned char found_left=0;
unsigned char found_straight=0;
unsigned char found_right=0;
//unsigned char found_back=0;
// Now read the sensorValues and check the intersection type.
const uint8_t SensorCount = 8;
uint16_t sensorValues[SensorCount];
qtr.read(sensorValues);
// Check for left and right exits.
if((sensorValues[7] > 200 || sensorValues[6]> 200) && sensorValues[5] > 200 && sensorValues[4]> 200 && sensorValues[3]> 200 )
found_right = 1;
if((sensorValues[0] > 200 || sensorValues[1] > 200 )&& sensorValues[2] > 200 && sensorValues[3] > 200 && sensorValues[4] > 200)
found_left = 1;
set_Motors(30,30); //-30
delay(20); //50
/*// Drive straight a bit more - this is enough to line up our
// wheels with the intersection.
set_Motors(45,45);
delay(200);*/
// Check for a straight exit.
qtr.read(sensorValues);
if(sensorValues[2] > 200 || sensorValues[3] > 200 || sensorValues[4] > 200 || sensorValues[5] > 200)
//sensorValues[2] > 200 || sensorValues[3] > 200 || sensorValues[4] > 200 || sensorValues[5] > 200
found_straight = 1;
//set_Motors(30,30);
//delay(200);
//if(sensorValues[0] < 100 && sensorValues[1] < 100 && sensorValues[2] < 100 && sensorValues[3] < 100 &&
//sensorValues[4] < 100 && sensorValues[5] < 100 && sensorValues[6] < 100 && sensorValues[7] < 100)
//found_back = 1;
qtr.read(sensorValues);
// Check for the ending spot.
// If all three middle sensorValues are on dark black, we have
// solved the maze.
if(sensorValues[2] > 300 && sensorValues[3] > 300 && sensorValues[4] > 300 && sensorValues[4] > 300 )
break;
// Intersection identification is complete.
// If the maze has been solved, we can follow the existing
// path. Otherwise, we need to learn the solution.
unsigned char dir = select_turn(found_right, found_straight, found_left);
// Make the turn indicated by the path.
Turn(dir);
// Store the intersection in the path variable.
//path[path_length] = dir;
//path_length ++;
// You should check to make sure that the path_length does not
// exceed the bounds of the array. We'll ignore that in this
// example.
// Simplify the learned path.
//simplify_path();
}
}
I am just only executing the dry run part. plz, guide me what to do.
Thanks for sharing with us. I wish to try it someday.
Unfortunately, debugging or helping write code is beyond the scope of our technical support, but I gave it a brief look, and it looks like your program might be unfinished (or perhaps you missed something when porting it over). For example, I do not see any logic for setting the found_left, found_right', or found_straight` variables when an intersection is identified, so they are always 0.
You might try going through the 3pi code you referenced and your code side-by-side so you can catch any other differences between them.
Brandon
Thanks for sharing your project, Kumar.